Retina contains a large number of light sensitive cells called rod cells and cone cells. The rod cells respond only to the intensity of light, while the cone cells respond to the colours of an object. There are 3 types of cone cells which are sensitive to red, blue and green colours to different extent i.e. when a red light falls on the retina then it mainly stimulates the red sensitive cone cells. These cone cells then send the information to brain in the form of electric signals through optic nerve. This gives rise to the sensation of that particular colour in our brain.
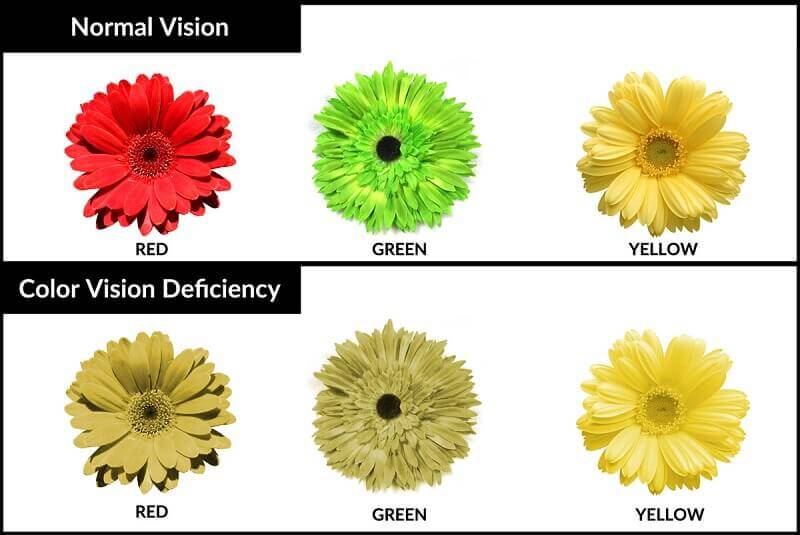
Sometimes, some particular types of cone cells are absent in a person due to which that person cannot see that particular colour. This condition is called colourblindness. Colourblindness may be defined as the inability of a person to distinguish between certain colours. For example, if a person doesn’t possess red-green sensitive cone cells then he cannot distinguish these colours from other colours. Colour blindness is a hereditary or genetic disorder which is not curable.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- How do we see colours?
- What is colourblindness?
- What is significance of rod cells and cone cells in human eye.
