It is commonly observed that the individuals of a species are alike, e.g. humans resemble one another and so do the monkeys and dogs. The reason for this resemblance is that the humans are produced by humans alone. In the same ways monkeys are produced by monkeys and dogs are produced by dogs. Often children resemble their parents or grandparents. This resemblance of characters of children with their parents is due to the transmission of these characters from parents to their offsprings. But we also observe that the children don’t resemble exactly to their parents. In other words the children have some individual characters, in which they differ from their parents and also from each other. This difference of structure, size, colour, function and behaviour in the individuals of the same species and also in the offsprings of the same parents is called variation. Thus variation can be defined as the differences in characters among the individuals of a species. That is why some humans are tall while some are less tall, some individuals have fare complexion while some other has dark complexion.
We can well understand the concept of variation with the help of following example. Suppose a father has good height, fare complexion, cleft chin, black hair, snub nose, and brown eyes, while the mother has short height, dark complexion, pointed chin, brown hair, sharp pointed nose and black eyes. As the children inherit some characters from father and some characters from mother, so the children produced by this couple may have following variations.
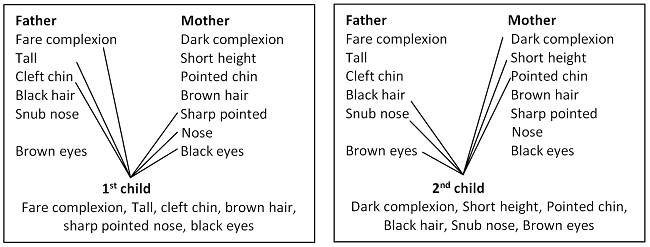
The 1st child may inherit fare complexion, height and cleft chin from father and brown hair, sharp pointed nose and black eyes from mother. On the other hand the 2nd child may inherit black hair, snub nose and brown eyes form father and dark complexion, short height and pointed chin from mother. In this way the variation will appear between two children of the same parents.
Types of Variations
The variations can be classified into two types:
1. Environmental variations
2. Hereditary variations
1) Environmental Variations
The variations which are produced in an organism due to the change in temperature, habitat, climate, food or any other atmospheric conditions are called as environmental variations.
2) Hereditary Variations
The variations which are produced in an organism due to the change in genetic make up of a person are called genetic variations.
Significance of Variations
Following are the significances of variations:
- Variations help in evolution i.e. variations help in the formation of new species.
- Variations help an organism in adopting itself according to the changing environment.
- Variations are the base of genetics.
Mutations
The process by which a gene or a chromosome changes structurally is called mutation. The term mutation was coined by Hugo de Vries. Mutations are common in nature. These can cause variations in hair colour, eye colour, skin colour and many others in the different members of a population.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- Define variations.
- Explain types of variations.
- What is significance of variations?
- What do you meant by mutation?
