Atomic Number
Definition of Atomic Number: Atomic number of an element is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. For example,
Atomic Number of Carbon: There are 6 protons present in the nucleus of carbon atom so the atomic number of carbon element is 6. The atomic number of an element is always represented by letter Z. thus,
Atomic Number (Z) = No. of protons
Mass Number
Definition of Mass Number: Mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. For example,
Mass Number of Carbon: There are present 6 protons and 6 neutrons in the nucleus of carbon atom, so mass number of carbon element is 12. The mass number of an element is always represented by letter A. thus,
Mass Number (A) = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
To see periodic table with mass number click here
Representation of Atomic Symbol of an Element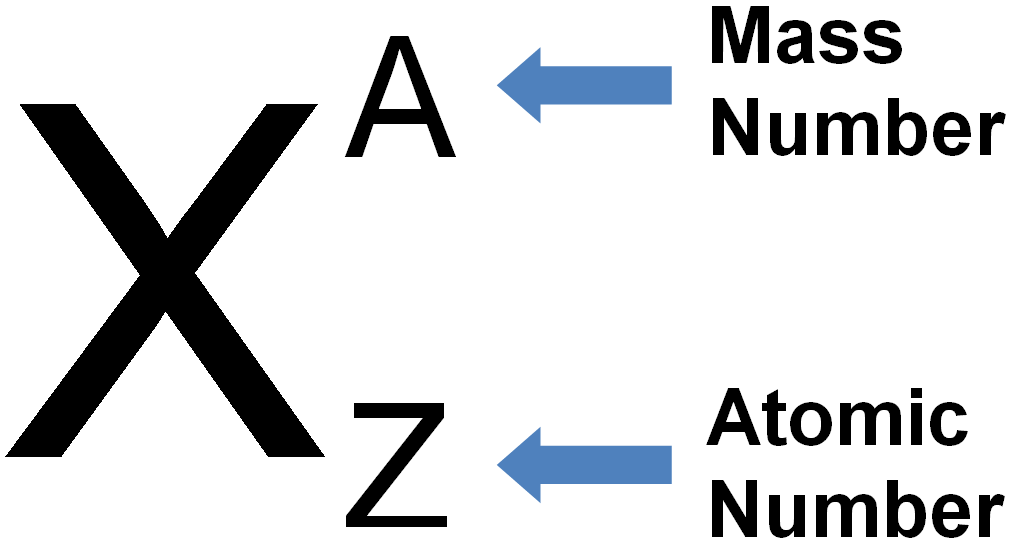
Representation of Atomic Symbol of Carbon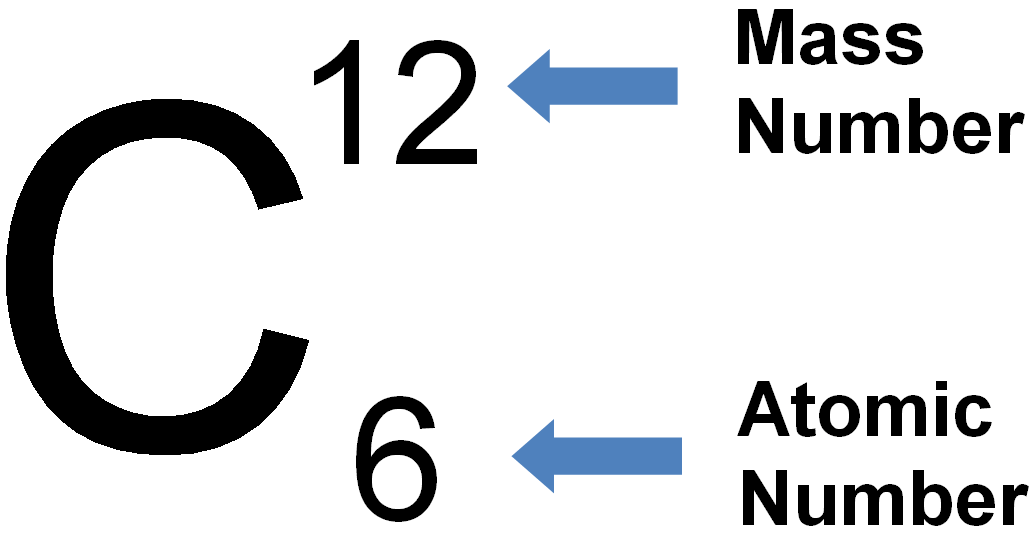
Calculation of number of neutrons from mass number and atomic number
The number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated from the known values of mass number and atomic number of that element using following expression:
Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number
Or number of neutrons = A – Z
For example, the number of neutrons in carbon can be found by using this formula. Carbon has mass number 12 and atomic number 6. By subtracting these values from each other we get the number of neutrons in carbon.
Number of neutrons in carbon = mass number of carbon – atomic number of carbon
Number of neutrons in carbon = 12 – 6
Number of neutrons in carbon = 6
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is mass number?
- How to find mass number of an element?
- Give atomic number definition.
- Give mass number definition.
- How to find the number of neutrons in an element?
