Budding may be defined as the process in which a small part of the body of the parent organism grows out as a small projection called ‘bud’ which when detaches becomes a new organism.
This method of asexual reproduction is found in hydra, sponges, flatworms and yeast.
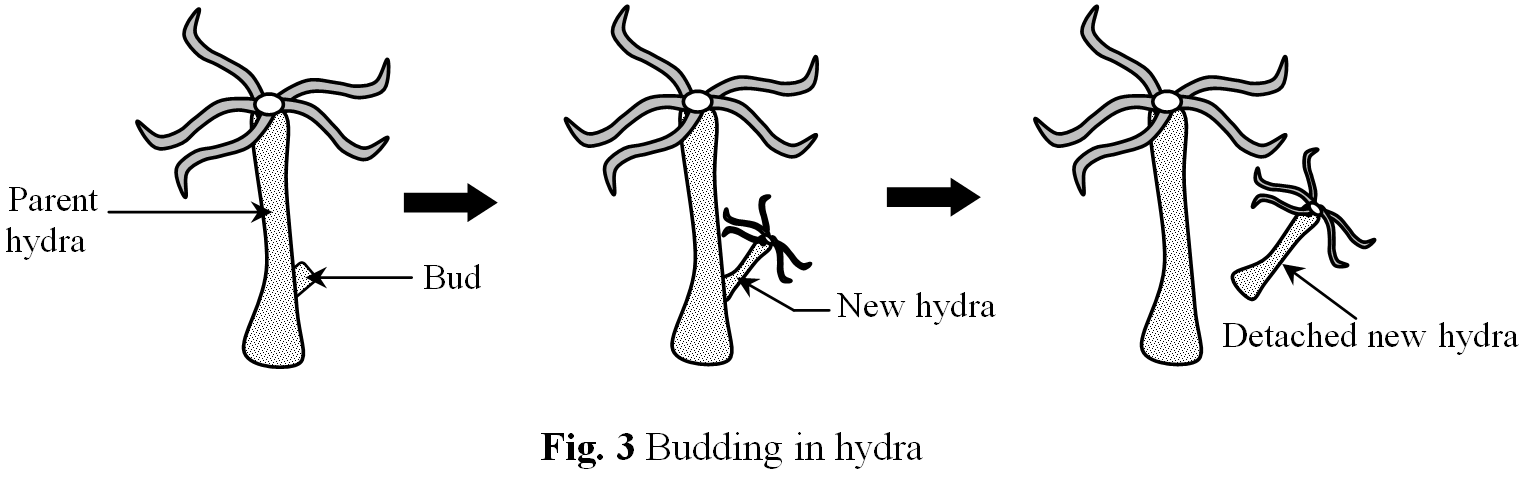
Budding in hydra
In hydra a small outgrowth which is called ‘bud’ is produced from the parent hydra. This bud drives nourishment from the parent hydra and grows. Ultimately it detaches from parent hydra and becomes an independent animal.
Budding in yeast
Yeast is a unicellular, non green fungus which reproduces by budding. In yeast first of all a small bud appears as an outgrowth from the body of the parent. Then the nucleus of the parent yeast divides into two parts and one nucleus shifts into the bud. In the end, the newly formed bud separates and grows into a new yeast cell.
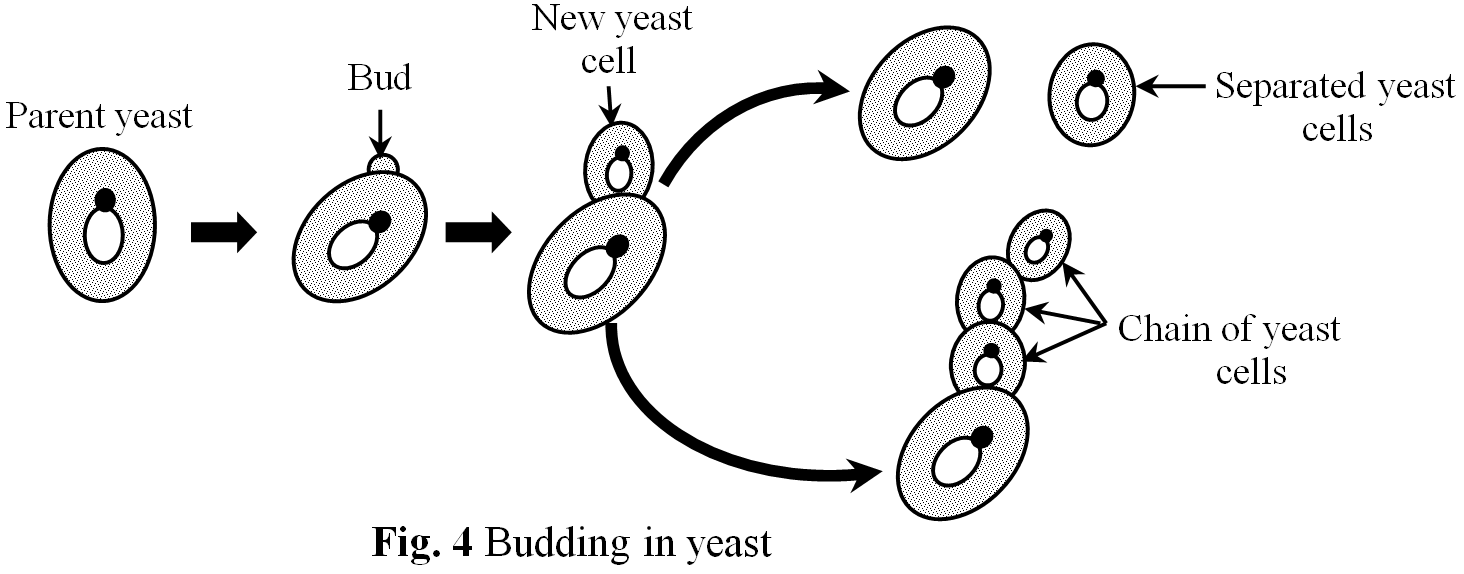
The process of budding is fast in yeast, and often the first bud starts forming new buds before getting detached from parent yeast cell. In this way a small chain of buds is formed on parent yeast cell, which ultimately breaks and all the buds form new yeast cells.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is budding?
- Explain various steps of budding in yeast.
- Explain various steps of budding in hydra?
