A compound microscope is an optical instrument consisting of two convex lenses of short focal lengths which is used for observing the highly magnified images of tiny objects. The compound microscope can magnify the image of a tiny object up to 1000.

Principle of compound microscope
A compound microscope works on the principle that when a tiny object to be magnified is placed just beyond the focus of its objective lens, a virtual, inverted and highly magnified image of the object is formed at the least distance of distinct vision from the eye held close to the eye piece.
Construction of compound microscope
A compound microscope consists of two convex lenses: an objective lens O of small aperture and an eye piece E of large aperture. The lens which is placed towards the object is called objective lens, while the lens which is towards our eye is called eye piece. These two convex lenses i.e. the objective and the eye piece have short focal length and are fitted at the free ends of two sliding tubes at a suitable distance from each other. Although the focal length of both the objective lens and eye piece is short, but the focal length of the objective lens O is a little shorter than that of the eye piece E.
The reason for using the eye piece of large focal length and large aperture in a compound microscope is, so that it may receive more light rays from the object to be magnified and form a bright image.
Working of compound microscope
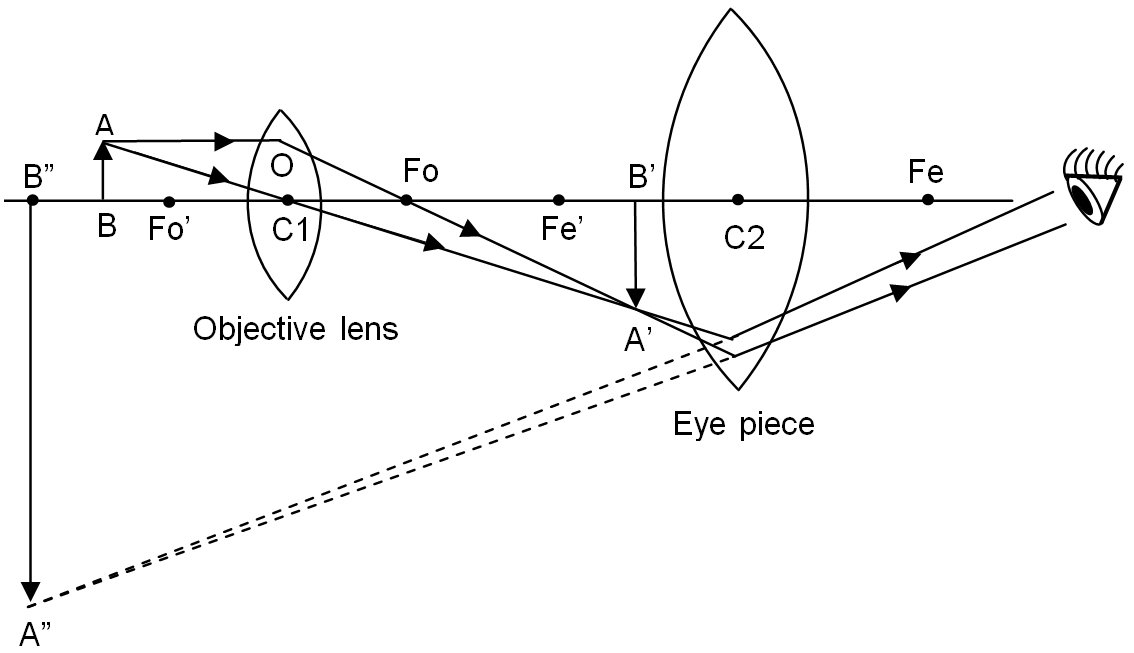
The ray diagram to show the working of compound microscope is shown in figure. A tiny object AB to be magnified is placed in front of the objective lens just beyond its principal focus fo’. In this case, the objective lens O of the compound microscope forms a real, inverted and enlarged image A’B’ of the object.
Now A’B’ acts as an object for the eye piece E, whose position is adjusted so that A’B’ lies between optical centre C2 and the focus fe’ of eye piece. Now the eye piece forms a final virtual, inverted and highly magnified image A”B”. this final image A”B” is seen by our eye hold close to eye piece, after adjusting the final image A”B” at the least distance of distinct vision of 25 cm from the eye.
Magnification of compound microscope
The magnification of compound microscope is given by:
m = 
where, D = Least distance of distinct vision (25 cm)
L = Length of the microscope tube
fo = Focal length of the objective lens
fe = Focal length of the eye-piece lens
Differences between Simple Microscope and Compound Microscope
| S No. | Simple Microscope | Compound Microscope |
| 1. | A simple microscope is also called magnifying glass. It is actually a convex lens of small focal length, which is used for seeing the magnified images of small objects. | A compound microscope is an optical instrument consisting of two convex lenses of short focal lengths which is used for observing the highly magnified images of tiny objects. |
| 2. | It consists of one convex lens. | It consists of two convex lenses of short focal length. |
| 3. | Its maximum magnifying power is 10. | Its maximum magnifying power is 1000. |
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is a compound microscope?
- Define objective lens.
- Define eye piece.
- How many lenses are used in compound microscope?
- What is magnification of compound microscope?
- Explain the principle, construction and working of compound microscope with the help of a diagram.
- Give differences between simple microscope and compound microscope.
