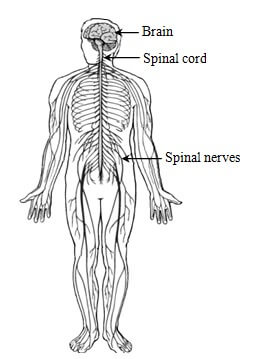
 The nervous system of human beings consists of brain, spinal cord and nerves.
The nervous system of human beings consists of brain, spinal cord and nerves.
Brain
The brain is the anterior part of the central nervous system. It is situated within the hard bones of the skull. It is wrapped in three separate membranes called meninges. The space present between these layers is filled with cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF). This fluid serves as a cushion and protects the brain from injuries and shocks. Six pairs of cranial nerves originate from the brain.
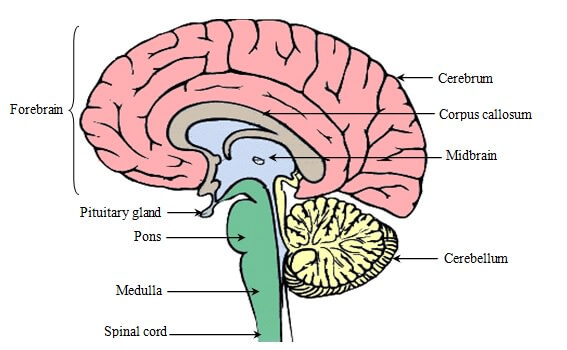
The brain of human beings is divisible in three major parts:
1. Forebrain
2. Midbrain
3. Hindbrain
1. Forebrain
Fore brain of human beings consists of cerebrum and olfactory lobes.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain which is dome shaped in structure. It is divided into two hemispheres called cerebral hemispheres by a deep fissure in the centre. The two cerebral hemispheres are connected to each other by a structure called corpus callosum. Each hemisphere of the cerebrum is further divided into four lobes.
- Frontal lobe:- This part of the cerebrum controls muscular activities and voluntary movements.
- Parietal lobe:- This part of the cerebrum controls general sensations such as taste, smell, pain, touch and temperature.
- Temporal lobe:- This part of the cerebrum is concerned with sense of hearing.
- Occipital lobe:- This part of cerebrum is concerned with sense of sight.
Olfactory Lobes
These are club shaped structures which are present at the anterior part of the brain. Olfactory lobes are concerned with sense of smell.
Functions of Forebrain
- It receives information from sense organs like eyes, ears, skin, nose and tongue.
- It interprets information and controls voluntary movements.
- It changes our behaviour on the basis of past experiences and memories.
- It maintains a balance between stimulus and response.
- It regulates the sense of sight, hearing, smell, touch, temperature and pain.
2. Midbrain
Mid brain of human beings is not further divided into parts. It is mainly concerned with sense of sight and hearing.
3. Hindbrain
Hind brain of human beings consists of cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
Functions of Hindbrain
- The cerebellum coordinates the movements and maintains posture.
- Pons is concerned with regulation of respiration.
- Medulla oblongata regulates heart beat, blood pressure, coughing, sneezing and rate of respiration.
Spinal Cord
Spinal cord is a cylindrical extension of the brain. It runs through a channel within the bony cage of vertebral column. Like brain, spinal cord is also wrapped in meninges. Thirty one pairs of spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord and reach every part of the body. The length of spinal cord varies from 37 to 45 cm. depending on the height of the person.
Functions of Spinal Cord
- It conducts nerve impulses from every part of the body to brain and carries messages back again.
- It regulates the reflex actions like instant removal of hands from a hot object.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- Write a note on meninges.
- Mention the functions of fore brain.
- Explain nervous system of human beings.
- What are the functions of medulla oblongata?
- Write the functions of any one part of hind brain.
- What are the functions of cerebral hemispheres?
- What is cerebrospinal fluid? What are functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
- Name the structure which joins the two cerebral hemispheres with each other.
