Neuron – Unit of Nervous System
The nervous system of animals consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons or nerve cells. Function of neuron or nerve cells is to carry information from receptors to brain and then from brain to effectors in the form of electrical signals. The passing of information through neurons in the form of electrical signals is called nerve impulse. Thus, a neuron is a functional and structural unit of nervous system. Neuron is the largest cell present in the body. It consists of three parts:
1. Cell body
2. Dendrites and
3. Axon
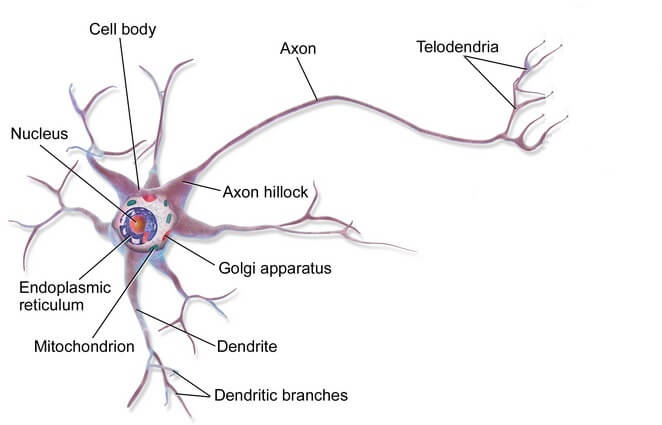
Cell body
A cell body is an irregular structure having cytoplasm and nucleus.
Dendrites
Dendrites are short and branched fibres which stretch out from the cell body.
Axon
Axon is a long fibre which also extends from the cell body. It carries messages in the form of electrical signals to other cells. It is enclosed in a sheath of protein myelin, which insulates them and helps to increase the speed at which they carry signals.
Neurons do not connect with each other directly. There is always a small gap between two neurons. This gap is called synapse. Information is passed from one neuron to another across the gap by a chemical substance called neurotransmitter.
Types of Neurons
There are three types of neurons:
- Sensory Neurons: These carry information from receptors to central nervous system (brain & spinal cord)
- Motor Neurons: These carry information from central nervous system to effectors.
- Association Neurons: These link sensory neurons to motor neurons.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is a neuron?
- What is synapse?
- What is a nerve impulse?
- What is a neurotransmitter?
- Explain structure of a neuron.
- Draw the diagram of a neuron.
- Explain different types of neuron.
- What is the function of neurons or nerve cells?
