The phenomenon of radioactivity involves the release of alpha, beta and gamma rays by the disintegration of a heavy nucleus. When a radioactive substance emits alpha or beta particles it changes into other element. The process of conversion of one element into another by emitting alpha or beta particles is called transmutation.During transmutation some mass of radioactive substance changes into radiations (energy). So, mass of radioactive substances decreases spontaneously over period of time. That is why this process is also called radioactive decay or nuclear decay.
Let’s discuss it in more detail.
1. Alpha Decay
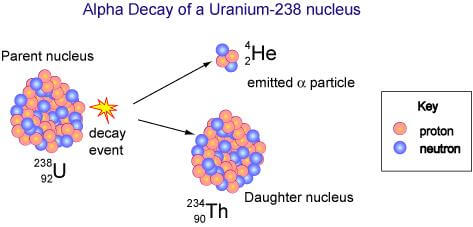
When a radioactive element emits an alpha particle it leads to the formation of a new element whose atomic number is decreased by 2 and mass number is decreased by 4. For example, when an atom of U-238 disintegrates to emit an alpha particle, it changes to thorium element.
92U238 ![]() 90Th234 + 2He4
90Th234 + 2He4
Uranium Thorium Alpha particle
2. Beta Decay
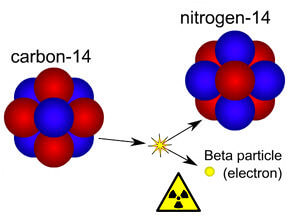
When a radioactive element emits a beta particle it leads to the formation of a new element whose atomic number is increased by 1 without any change in its mass. For example, when an atom of carbon-14 emits a beta particle it changes into nitrogen.
6C14 ![]() 7N14 + -1e0
7N14 + -1e0
Carbon Nitrogen Beta particle
3. Gamma Decay
The mass and charge of gamma rays is zero, so emission of gamma rays from radioactive elements does not change it into other elements because there is no change in its atomic number or mass number.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is radioactive decay?
- What is alpha decay? Give an example.
- What is beta decay? Give an example.
- What is gamma decay? Give an example.
- What is definition of transmutation?
