The process by which the sex of a person is determined is called sex determination. The sex of a person is determined by sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes in human beings are present in 23 pair. Both the sexes either male or female contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes which are similar in both the males and females.
The sex chromosomes are similar in females and are called XX. This means that females can produce only one kind of eggs each having X chromosome. On the other hand sex chromosomes of males are dissimilar and are called as XY. The chromosome Y is much smaller in size as compared to chromosome X. So a male can produce two types of sperms out of which half the sperms will have X chromosomes while the other half will have the Y chromosome.
Determination of Sex of Human Child
The sex of a child depends on the fusion of different kinds of sperms with eggs during fertilization. As sperms are of two types, so the following two cases may arise
Case 1 – If the sperm containing X chromosome fuses with the egg containing X chromosome then the child born will be a girl having XX combination of sex chromosomes.
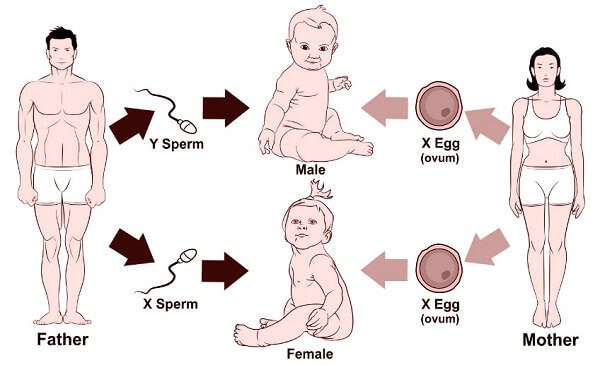
Case 2 – If the sperm containing Y chromosome fuses with the egg containing X chromosome then the child born will be a boy having XY combination of sex chromosomes.
Sex Determination in Reptiles
The sex of reptiles can be determined with temperature. For example, if the temperature of eggs of lizards is raised then male lizards are formed on the other hand if the temperature of eggs of lizards is lowered then female lizards are produced. In the same way, if the temperature of eggs of tortoise is increased then it results in the formation of female tortoise, on the other hand, if the temperature of eggs of tortoise is lowered then it results in the formation of a male tortoise.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is sex determination?
- Explain how sex is determined in human beings.
- Explain sex determination in reptiles.
- Explain the significance of temperature in determination of sex in reptiles.
