All plants require water to survive. Plants absorb water present in the soil. The absorbed water is transported to all the parts of the plants (stems, leaves, flowers and fruits) by xylem vessels. Xylem is a complex tissue which consists of dead cells called xylem vessels and tracheids.
Xylem vessels
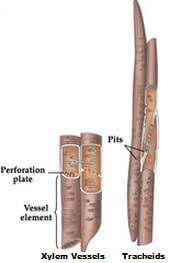
The xylem vessels are long tubes which help in transportation of water and provide mechanical support. Each xylem vessel is formed by end to end union of a large number of short, wide, lignified dead cells. In these cells both the nucleus and cytoplasm are absent. The end walls of these cells are often completely broken to form a long distance channel for transport of water. The cell wall of xylem vessels also possesses non-lignified thin areas called pits.
Tracheids
Tracheids are elongated dead cells having pointed ends and thick cell walls. Like xylem vessels, pits are also present in thick cell walls of tracheids. Water travel from one tracheids to other through pits.
Test Your Understanding and Answer These Questions:
- What is xylem?
- Describe transport of water in plants.
- Name the two kinds of cells of xylem.
- Write short notes on xylem vessels and tracheids.
- Name the various cells through which water move upwards to reach the leaves.
